Transformative improvements in performance, reliability, and scalability
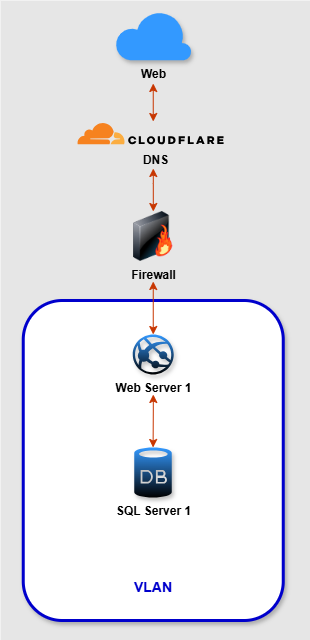
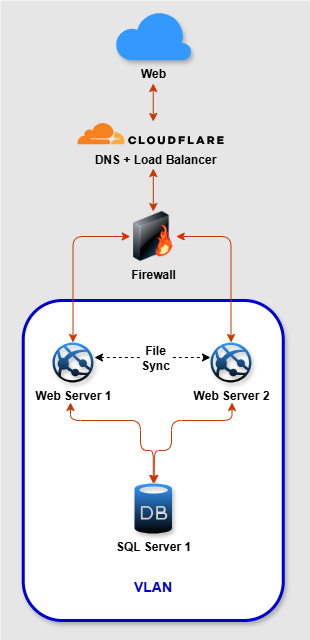
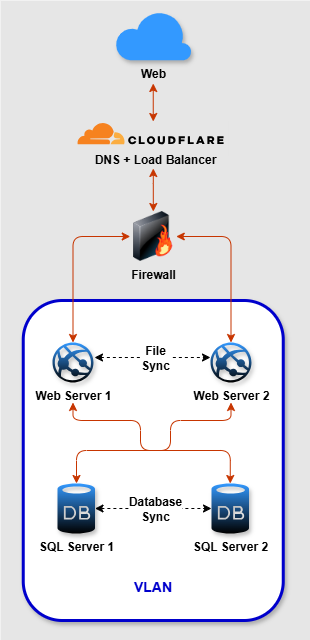
Navigator TMS is a transportation management software provider that helps trucking companies of all sizes improve their logistics. Since its inception, the company has embraced innovative solutions to meet the evolving demands of the trucking industry. Faced with the need for better performance and reliability, Navigator TMS partnered with xByte Cloud to overhaul its hosting environment. The result was high availability and fast service for clients across the country.